GOACON 2020
#GOACON #Rajkot
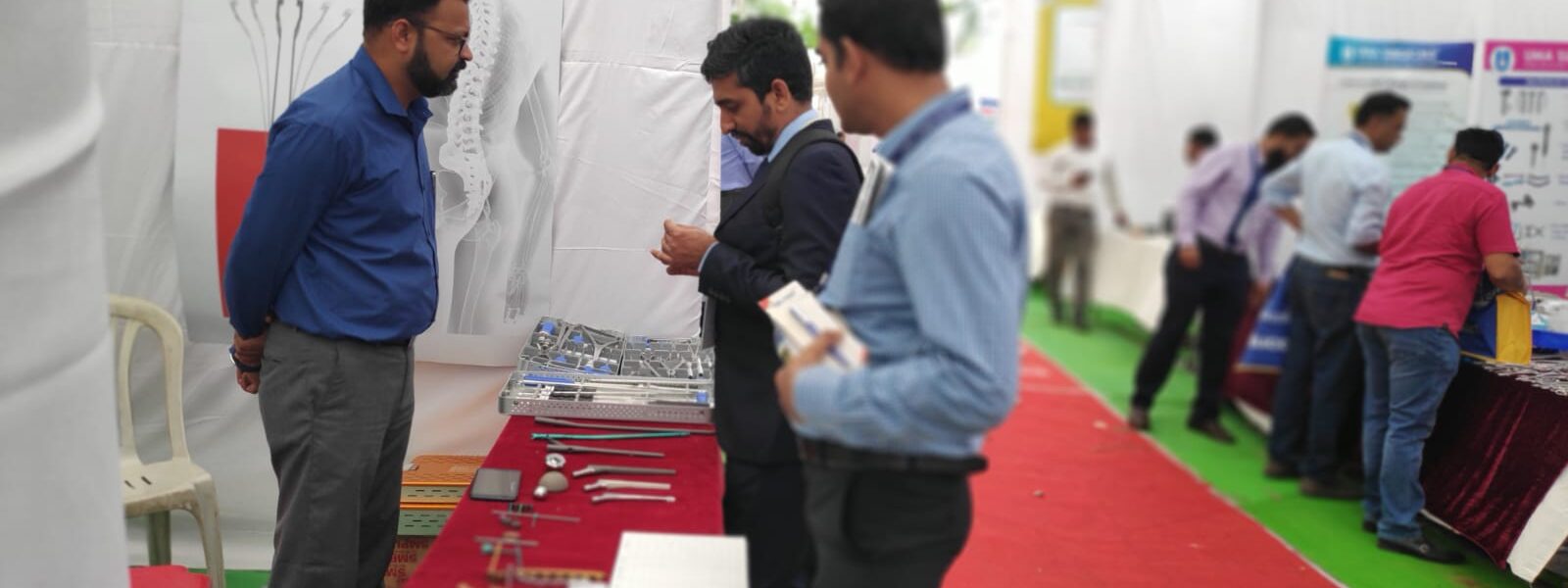
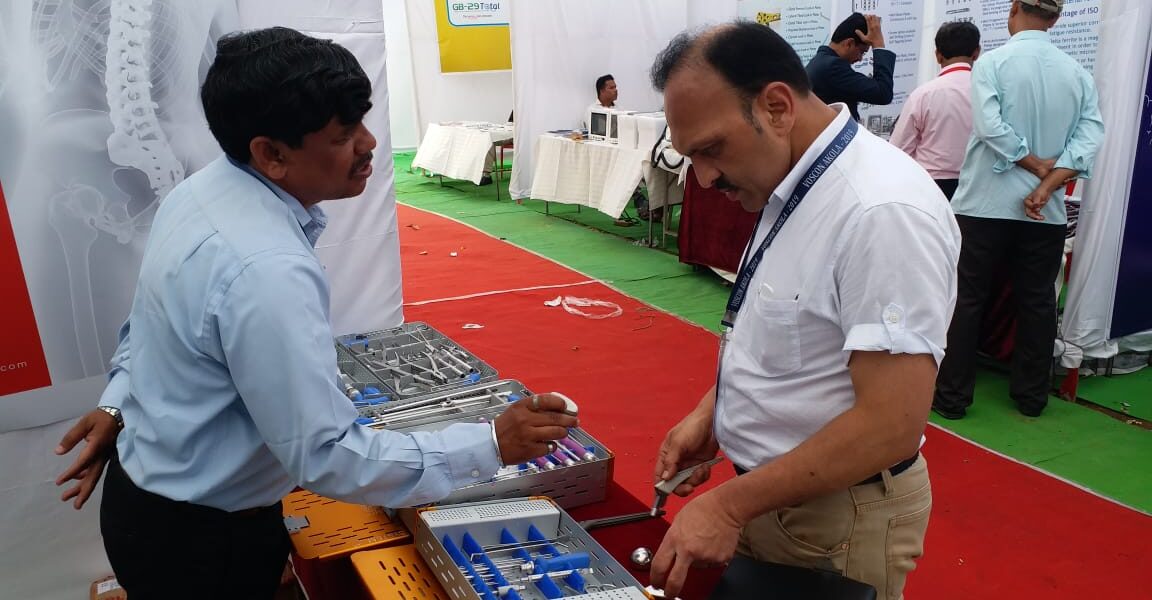
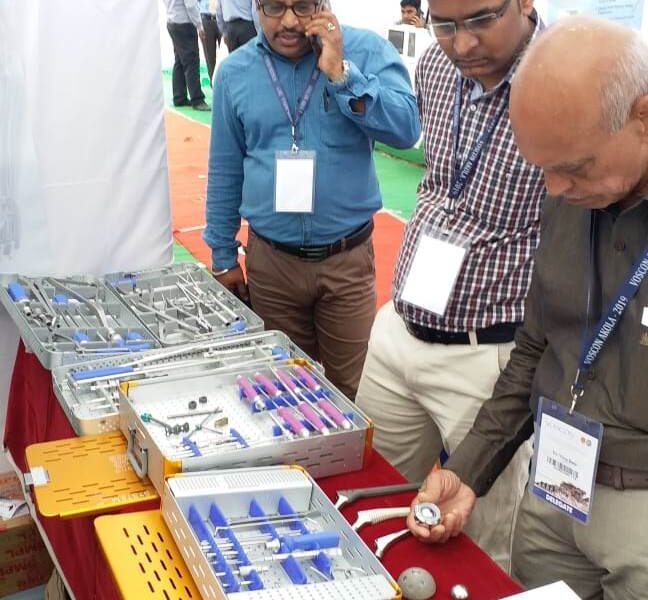
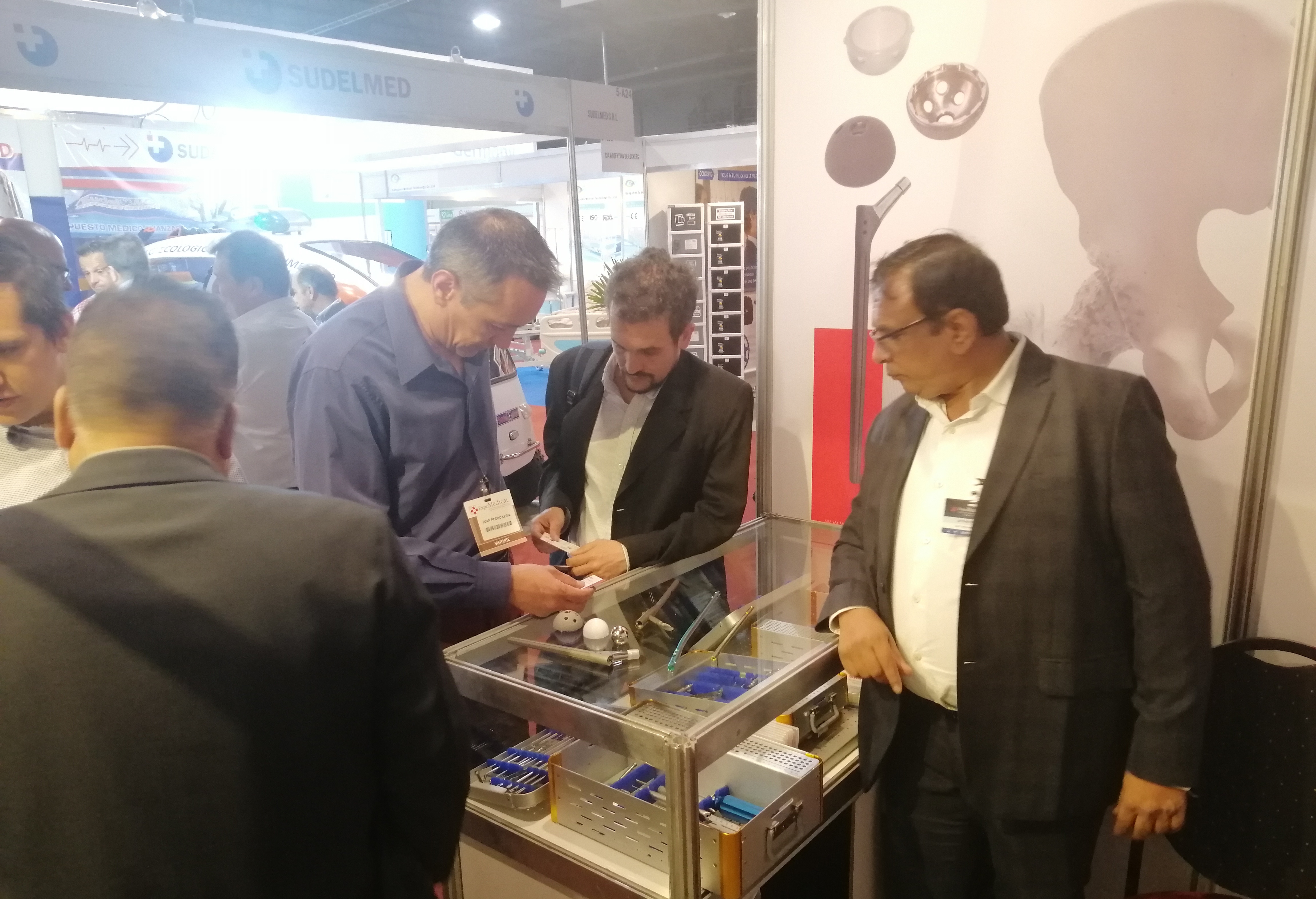
We Smit Medimed, Manufacturer & Exporter of the Orthopaedic Implants & Instruments.
We participated in GOACON 2020 Event held in Rajkot< Gujarat from 8th & 9th Feb, 2020.
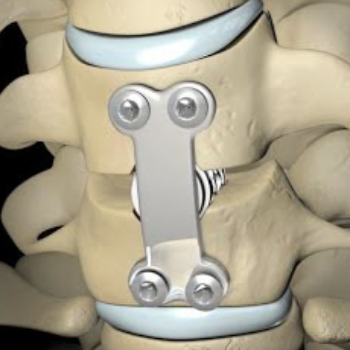
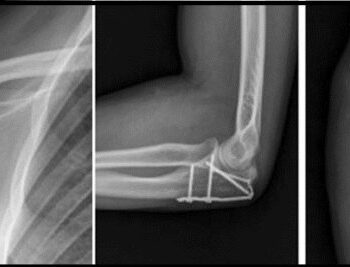
We exhibited our Spinal Implants, Trauma implants, Intramedullary nailing system & Hip & Knee Replacement system and instruments.