VOSCON 2019
VOSCON 2019
We participated in VOSCON 2019 Event held at City Sports Club(CSC) resort, NH-6, Amravti Road, Akola on 19th & 20th October 2019.
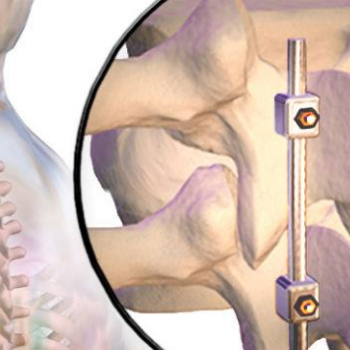
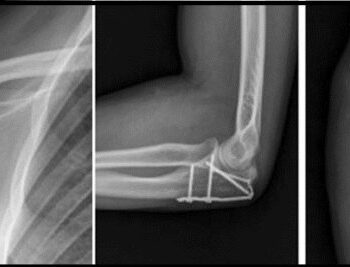
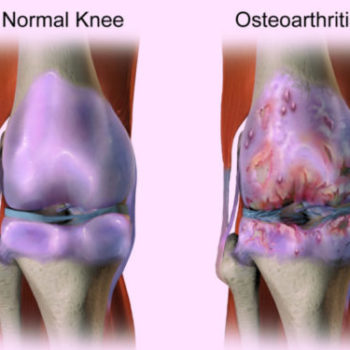
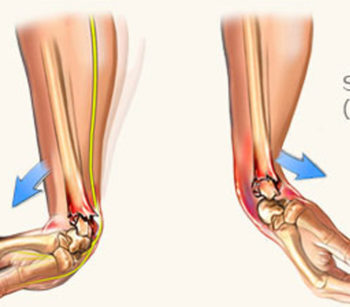
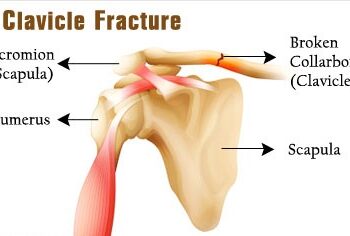
We exhibited our Spinal Implants, Trauma Implants, Intramedullary Nailing system, Hip & Knee Replacement System and instruments.