Femur Shaft Fractures (Broken Thighbone)
Our thighbone (femur) is the longest and strongest bone in our body. Because the femur is so strong, it usually takes a lot of force to break it. Motor vehicle collisions, for example, are the number one cause of femur fractures.
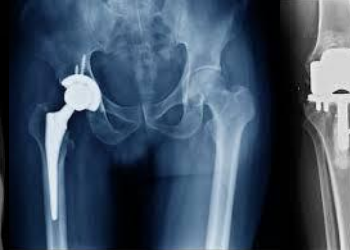
The long, straight part of the femur is called the femoral shaft. When there is a break anywhere along this length of bone, it is called a femoral shaft fracture. This type of broken leg almost always requires surgery to heal.
Types of Femoral Shaft Fractures
Femur fractures vary greatly, depending on the force that causes the break. The pieces of bone may line up correctly (stable fracture) or be out of alignment (displaced fracture). The skin around the fracture may be intact (closed fracture) or the bone may puncture the skin (open fracture).
Doctors describe fractures to each other using classification systems. Femur fractures are classified depending on:
- The location of the fracture (the femoral shaft is divided into thirds: distal, middle, proximal)
- The pattern of the fracture (for example, the bone can break in different directions, such as crosswise, lengthwise, or in the middle)
- Whether the skin and muscle over the bone is torn by the injury
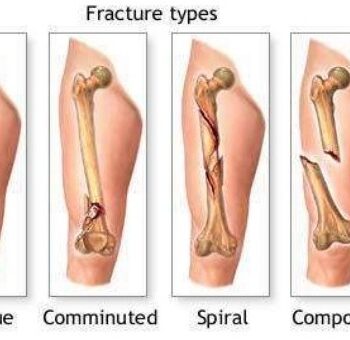
The most common types of femoral shaft fractures include:
Transverse fracture. In this type of fracture, the break is a straight horizontal line going across the femoral shaft.
Oblique fracture. This type of fracture has an angled line across the shaft.
Spiral fracture. The fracture line encircles the shaft like the stripes on a candy cane. A twisting force to the thigh causes this type of fracture.
Comminuted fracture. In this type of fracture, the bone has broken into three or more pieces. In most cases, the number of bone fragments corresponds with the amount of force needed to break the bone.
Open fracture. If a bone breaks in such a way that bone fragments stick out through the skin or a wound penetrates down to the broken bone, the fracture is called an open or compound fracture. Open fractures often involve much more damage to the surrounding muscles, tendons, and ligaments. They have a higher risk for complications—especially infections—and take a longer time to heal.
Cause
Femoral shaft fractures in young people are frequently due to some type of high-energy collision. The most common cause of femoral shaft fracture is a motor vehicle or motorcycle crash. Being hit by a car while walking is another common cause, as are falls from heights and gunshot wounds.
A lower-force incident, such as a fall from standing, may cause a femoral shaft fracture in an older person who has weaker bones.
Symptoms
A femoral shaft fracture usually causes immediate, severe pain. You will not be able to put weight on the injured leg, and it may look deformed—shorter than the other leg and no longer straight.
Credit to: orthoinfo